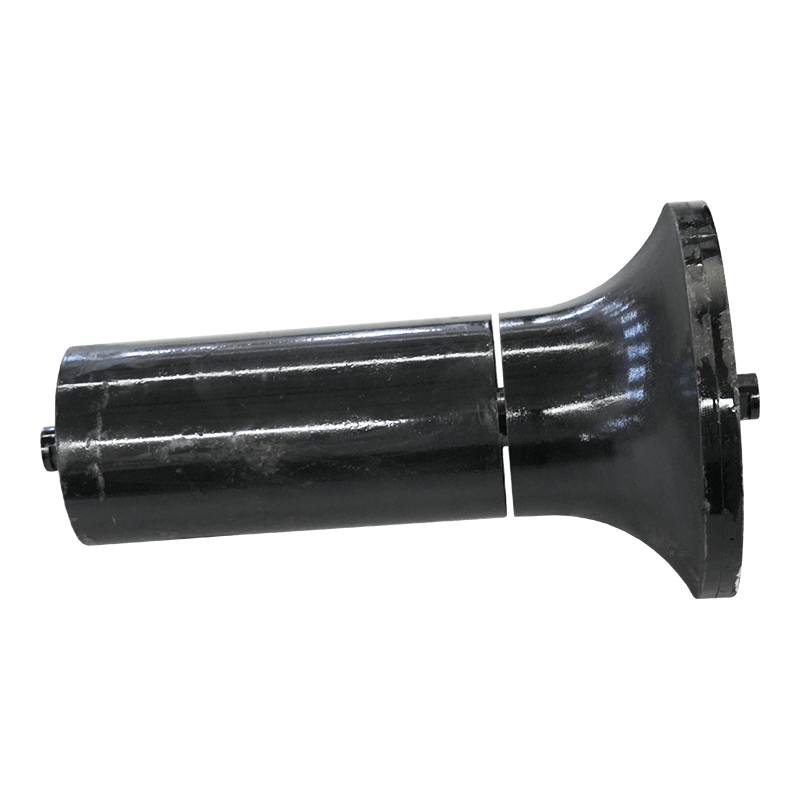
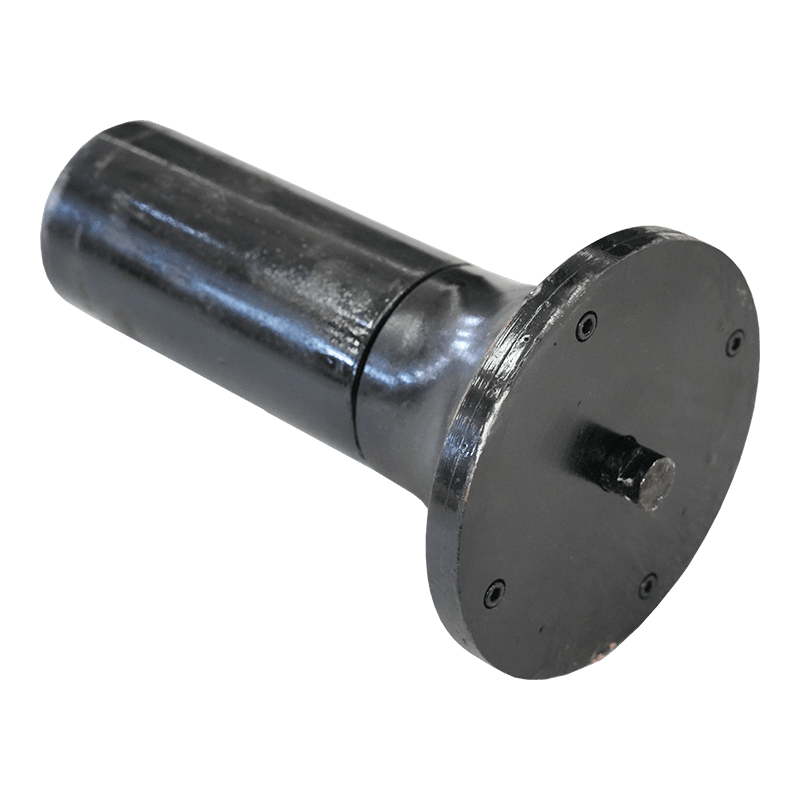
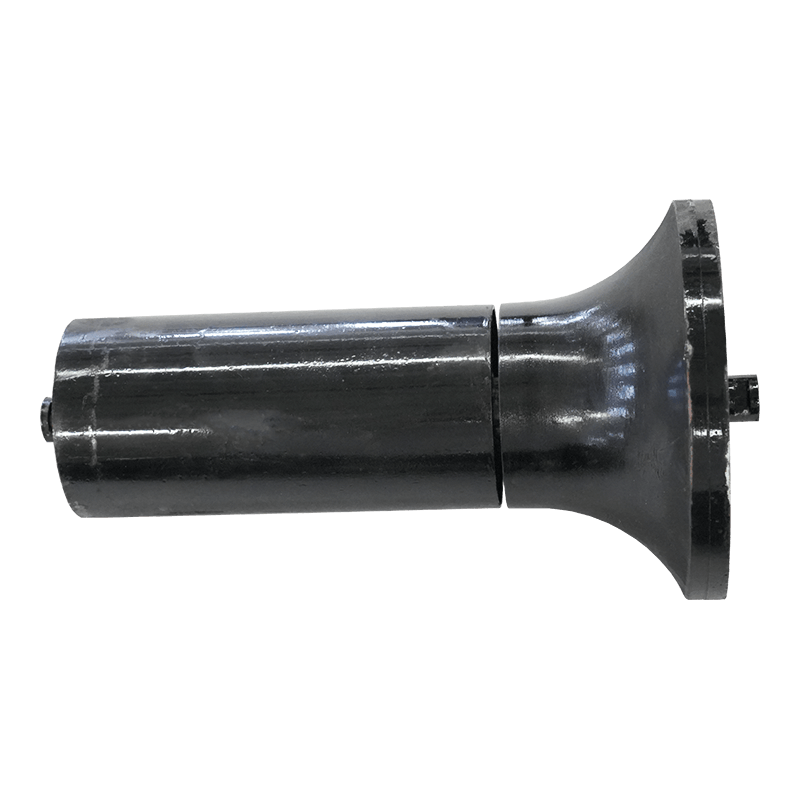
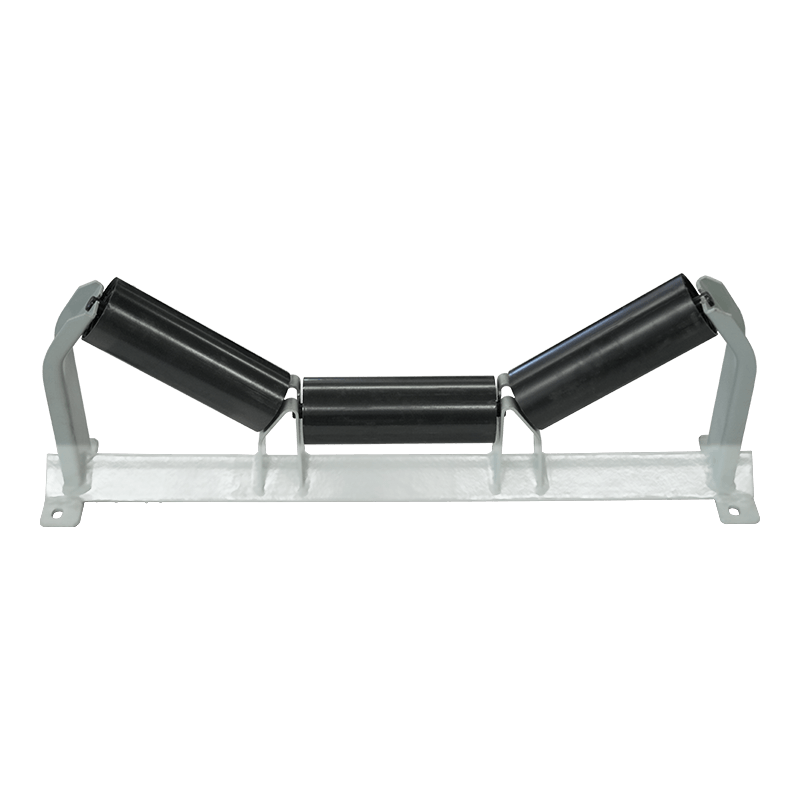
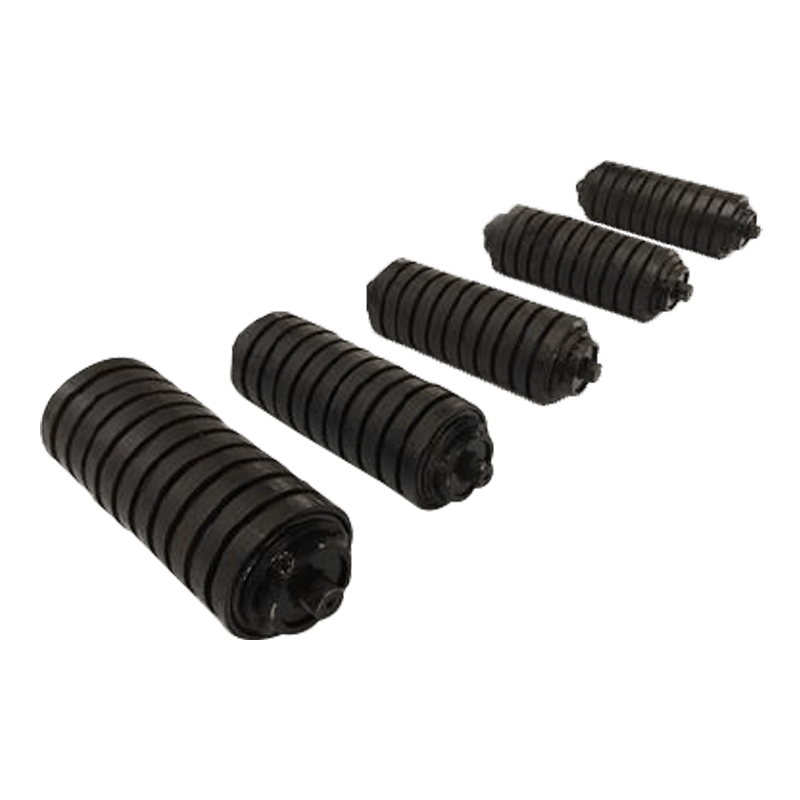
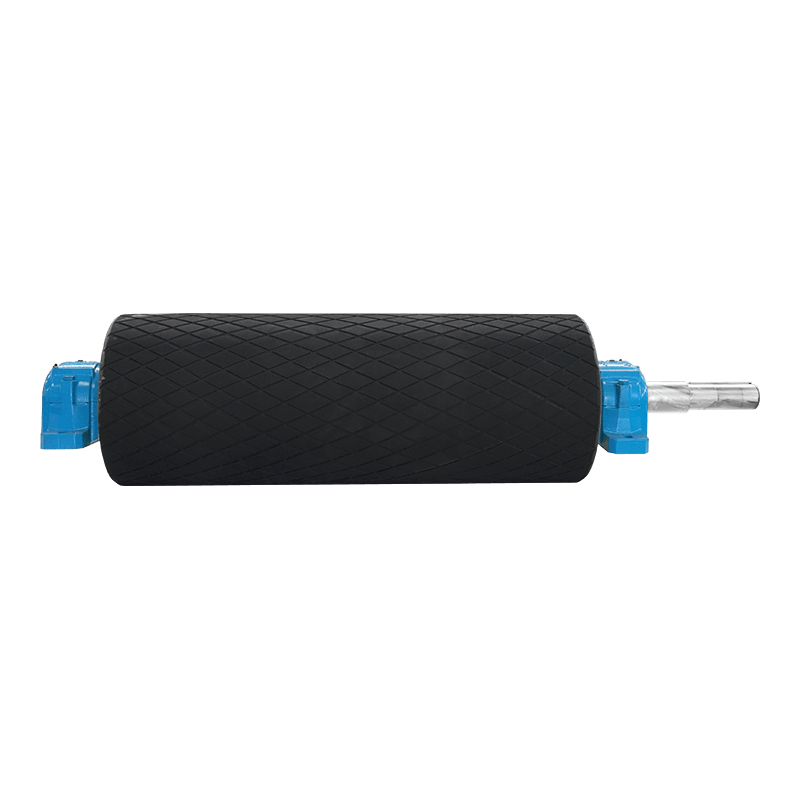
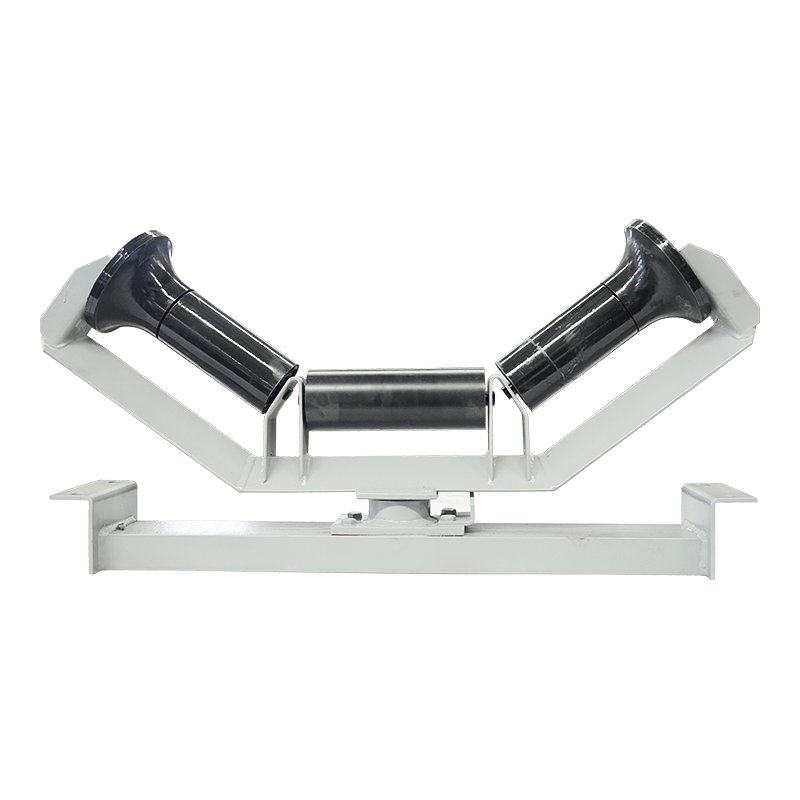
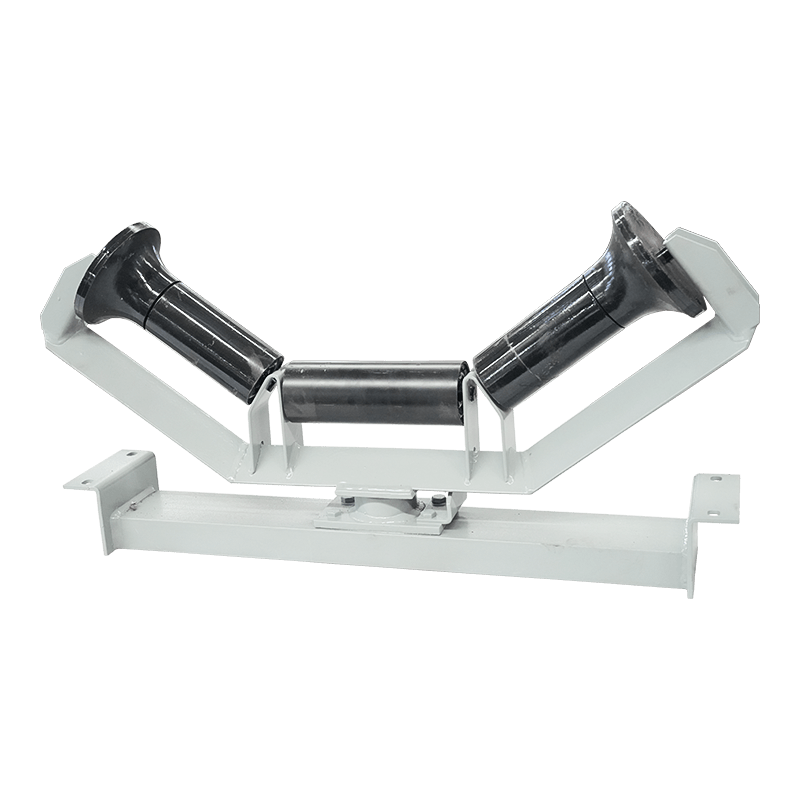
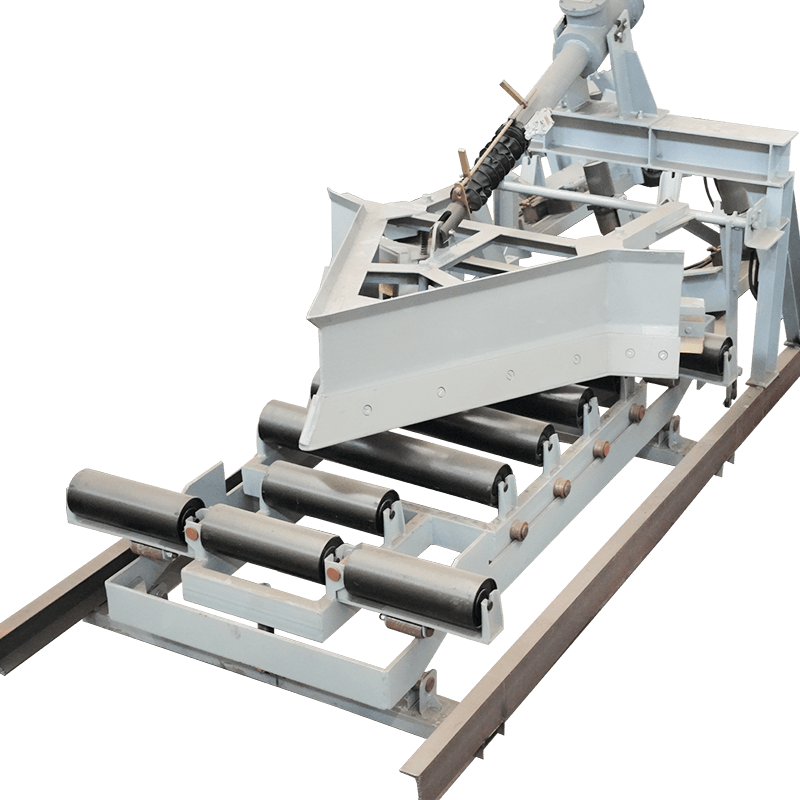
Belt Conveyor Tapered Idler
The tapered roller is a common conveyor belt auxiliary equipment, mainly used in the transportation, transportation and storage of materials. It consists of multiple cone-shaped rollers and a support structure, and the movement of materials is achieved through the rotation of the rollers. The working principle of the tapered roller is based on the friction of the material and the acceleration of gravity. When materials are transported through the conveyor belt, they are supported and pushed by the rollers, and at the same time friction is generated on the surface where the rollers contact the materials. This friction causes the material to move forward, gradually accelerating during the movement.
The biggest feature of the tapered rollers is that the gap between the rollers gradually shrinks and becomes tapered from large to small. This design allows the material to be gradually squeezed during movement, thereby achieving better conveying effects. The larger diameter rollers push the material, while the smaller diameter rollers are used to stabilize the movement of the materials. Through reasonable roller arrangement and appropriate taper angle, tapered rollers can achieve stable and efficient material transportation.

Specifications
Performance features:
Efficient and stable: The tapered structure of the tapered roller helps stabilize the movement trajectory of the material and improves the conveying efficiency.
Energy saving and environmental protection: The design of the tapered roller reduces the sliding friction of the material on the conveyor belt and reduces energy consumption.
Strong adaptability: The tapered roller can be adjusted and optimized according to different material characteristics and transportation needs, and has great adaptability.
Easy maintenance: The tapered roller has a simple structure and is easy to install and maintain, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Application: Mining, ports, food, warehousing
KEEP IN TOUCH

Our company focuses on the product R&D and investment, and with the great support from the government, has founded its research center of high lift conveyor engineering technology, and successively developed an extensive technical exchange and cooperation with many universities and famous organizations such as, Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, Northeastern University, Beijing Iron & Steel Design & Research Institute, Bejing Hoisting & Conveying Machinery Research Institute, German Contitch Company, Britain SBS Company, German KoCH Company etc.; and has successively obtained 22 national patents in the product R&D.
-

1. Why Clean Belt Conveyor Idlers? (Purpose and Benefits of Cleaning) Preventing Deviation: Dust and sticky materials (such as coal, clay, fertilizer, and grain) can adhere to the idler surface, formi...
READ MORE -

1. Situations Require Emergency Shutdown and Replacement (Red Line Safety Hazards) Loss of Structural Integrity:Deep cracks on the conveyor pulley surface (cracks large enough to fit a fingernail or g...
READ MORE -

1. Belt Conveyor Roller Surface Problems (1) Wear and Peeling of Surface Rubber Reasons:Normal wear: Long-term friction with the belt and material.Abnormal wear: The blade of the cleaner is too hard o...
READ MORE
Adjustment and optimization process of Tapered Idlers
1. Identify material characteristics
Material types: Understand the type of material being transported (such as ore, food, chemical products, etc.), because different materials have different fluidity and friction characteristics.
Material shape and weight: The shape (such as granular, block, powder, etc.) and weight of the material affect its behavior during transportation and determine the required roller shape and configuration.
2. Adjust the cone angle
Cone angle selection: Select the appropriate cone angle according to the characteristics of the material and the transportation speed. Generally speaking, a larger cone angle (such as 30 degrees) is suitable for materials with poor fluidity or heavier materials to help the material slide smoothly; a smaller cone angle is suitable for materials with good fluidity.
Dynamic adaptation: In actual applications, real-time adjustments may be required according to different working conditions and material characteristics to ensure the best transportation effect.
3. Optimize roller spacing
Roller spacing setting: Adjust the spacing between Tapered Idlers, usually between 100mm and 300mm, and set according to the size and weight of the material. Too large a spacing will cause the material to fall, and too small a spacing will increase friction and wear.
Uniform pressure distribution: Ensure that the layout of the rollers can evenly distribute the weight of the material and prevent roller damage caused by excessive local pressure.
4. Testing and evaluation
Operation test: After adjustment, conduct actual operation test to observe the flow and accumulation of materials. Evaluate the adjustment effect by monitoring transportation efficiency, material distribution and conveying speed.
Data analysis: Collect operation data and analyze the performance of materials on tapered rollers, including sliding speed, wear and material stability.
5. Feedback and improvement
Continuous optimization: According to the feedback from actual operation, make necessary fine-tuning and optimization, such as resetting the cone angle or adjusting the roller spacing.
Record and update: Record the success and failure lessons of the optimization process for reference and application in future projects.
6. Comprehensive consideration of environmental factors
Working environment: Consider the impact of ambient temperature, humidity and other factors on material characteristics and transportation process, and make corresponding adjustments when necessary.
Equipment maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain tapered rollers and related equipment to ensure that they operate in good condition and reduce failures and downtime.

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español