How to Determine Whether Belt Conveyor Troughing Idlers Need Replacement?
 2025.09.10
2025.09.10
 Industry News
Industry News
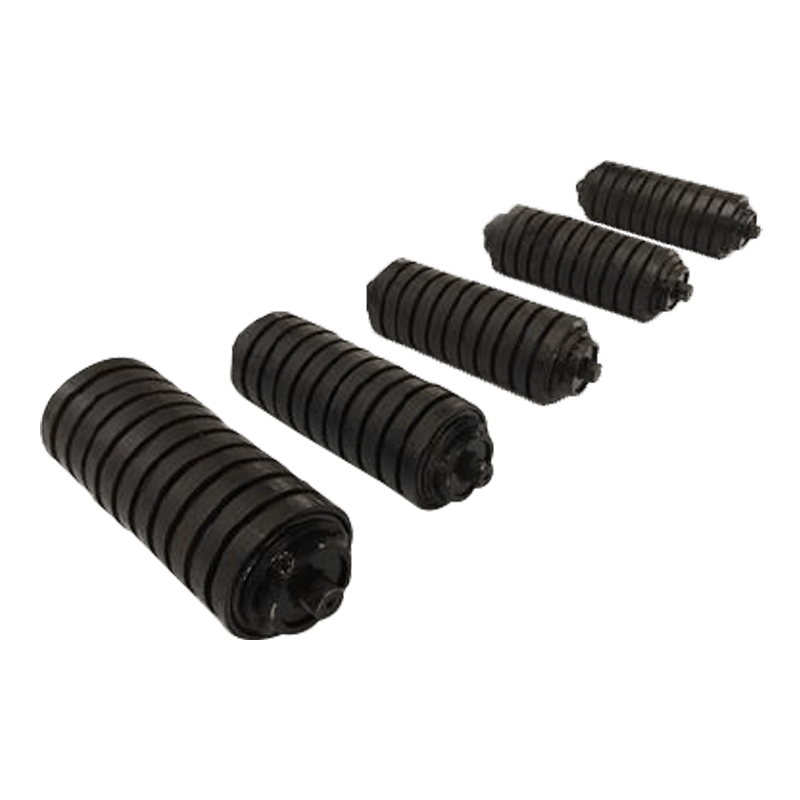
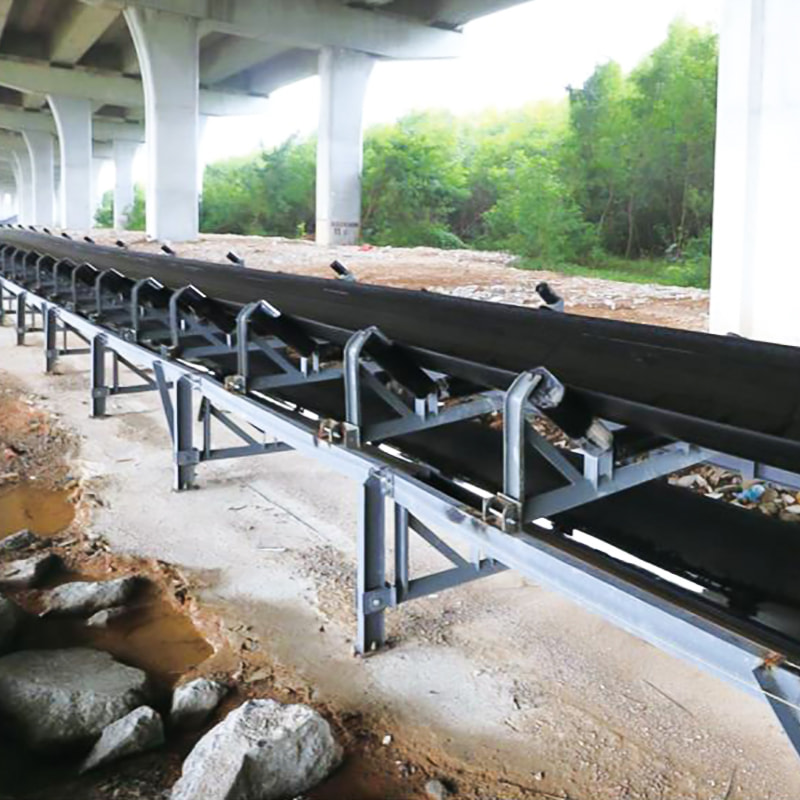
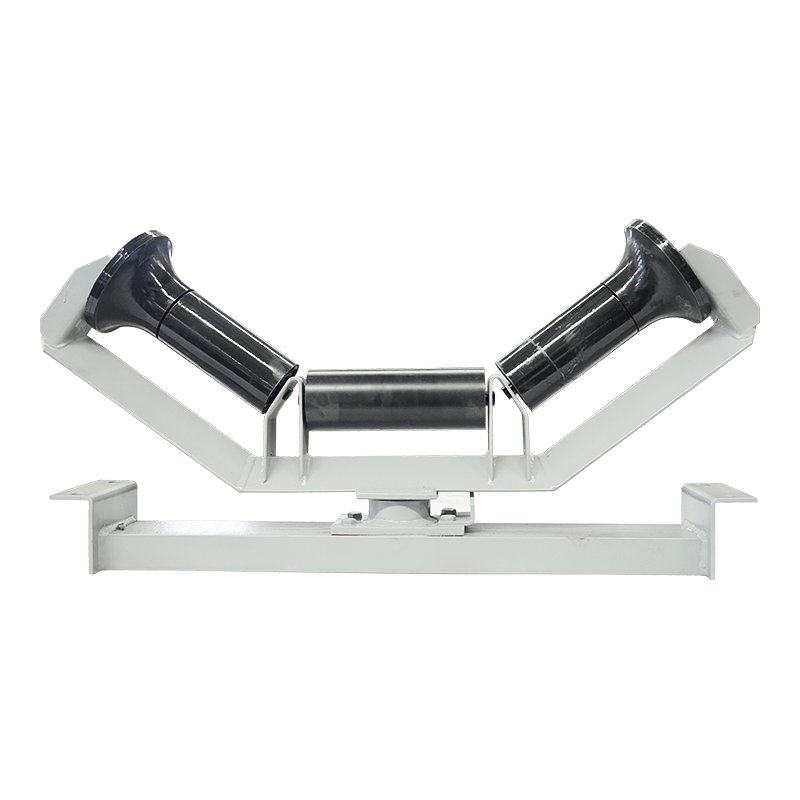
Belt conveyor troughing idlers are key components supporting the conveyor belt. Their condition directly affects conveying efficiency, energy consumption, and equipment life. Troughing idlers are widely used in open-air, dusty, and highly corrosive environments. They are essential for almost all heavy-load conveying applications. Troughing idlers are generally designed with a 30-degree trough angle and typically consist of two side idlers and one flat idler.
1. Appearance Inspection Criteria
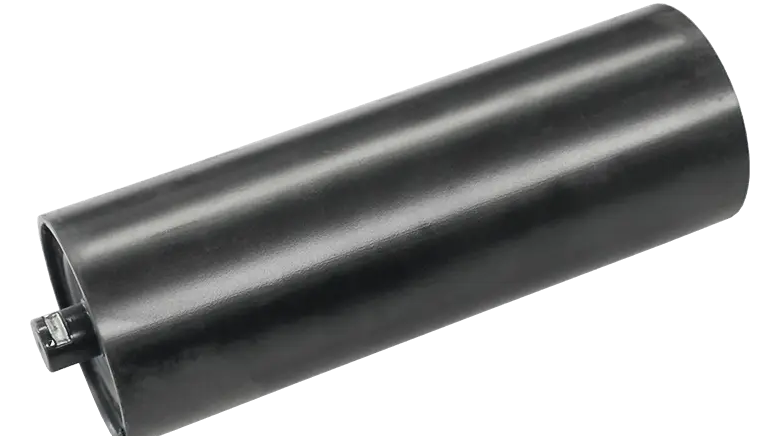
Roller Surface Wear
Replacement Criteria:
Rubber coating worn to the point where the metal core is exposed (impairing shock absorption and anti-slip properties)
Pits ≥ 2mm deep appear on the metal roller surface (causing belt deviation)
Inspection Method: Observe with a flashlight and feel for unevenness with your finger
Bearing Condition
Replacement Criteria:
Seal cap detached or severely rusted (causing lubrication failure)
Bearing seat deformed or cracked
Inspection Method: Pry open the seal cap to inspect grease contamination
Structural Deformation
Replacement Criteria:
Roller body curvature > 3mm/m (measured with a ruler)
Groove angle deformation causing the three roller sections to be non-aligned

2. Operating Condition Criteria
Abnormal Noise
Replacement Criteria:
Regular "clicking" sound during rotation (bearing ball damage)
Sharp metallic friction sound (bearing seizure)
Testing Tools: Auscultate with a mechanical stethoscope or screwdriver against your ear.
Rotational resistance test
Replacement criteria:
Manual rotation force > 5 N·m (normal: 1-2 N·m)
Autorotation < 1 rotation after stall (a healthy roller should be able to rotate 2-3 rotations)
Test method: Remove the roller and measure with a torque wrench.
Abnormal temperature
Replacement criteria:
Surface temperature > ambient temperature + 25°C (infrared thermometer).
Local overheating and blackening (grease carbonization).
3. Belt Operation Impact Assessment
Belt Deviation Correlation
Replacement criteria:
Adjustment of the guide device is ineffective, and the deviation position is fixed to a certain set of rollers.
Belt edge wear is jagged (friction caused by rollers not rotating).
Material spillage analysis
Replacement criteria:
Trough roller set is sunken in the middle, forming a "W" shape instead of a "U" shape.
Material spillage at a fixed location (roller out-of-roundness causing runout).

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español