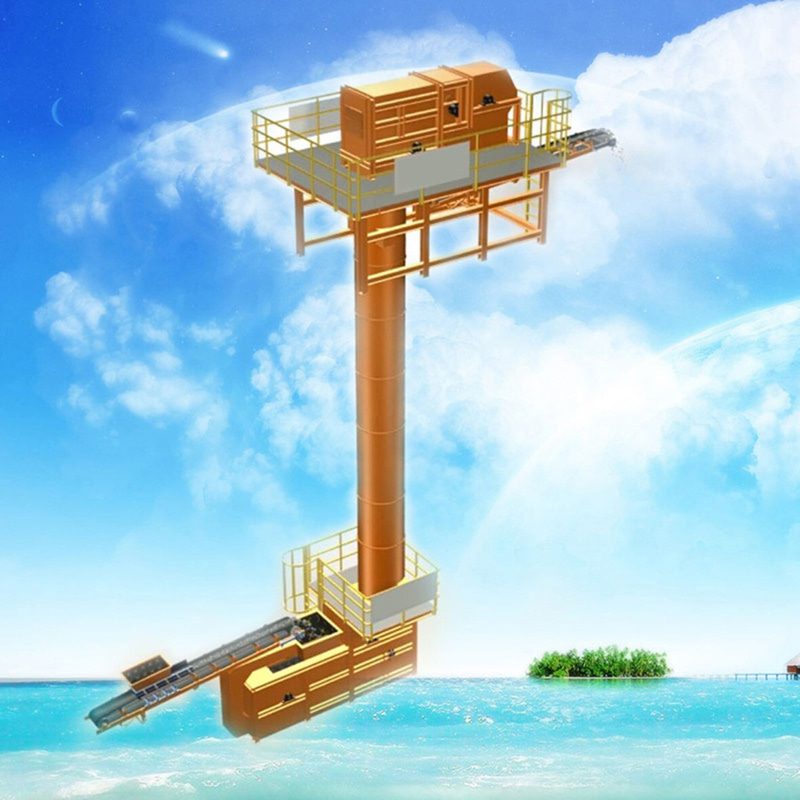
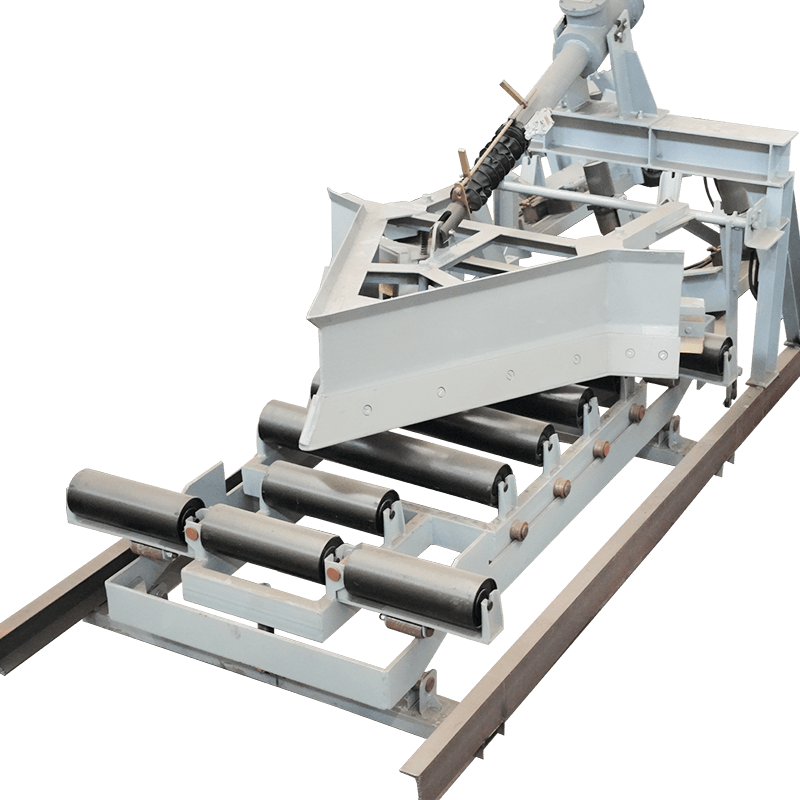
What is the function of a belt conveyor impact idler?
 2025.10.10
2025.10.10
 Industry News
Industry News
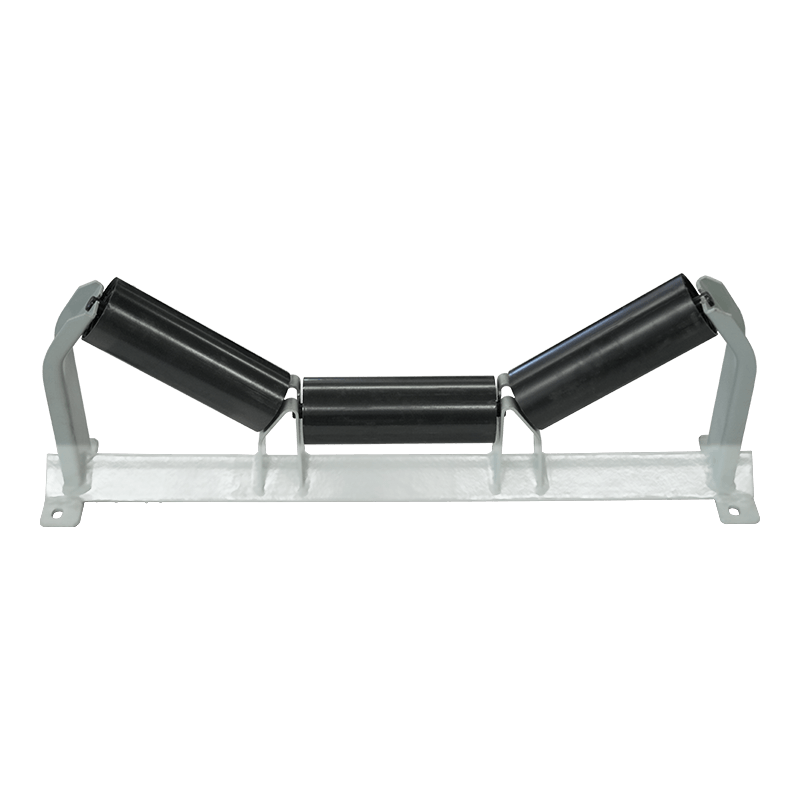
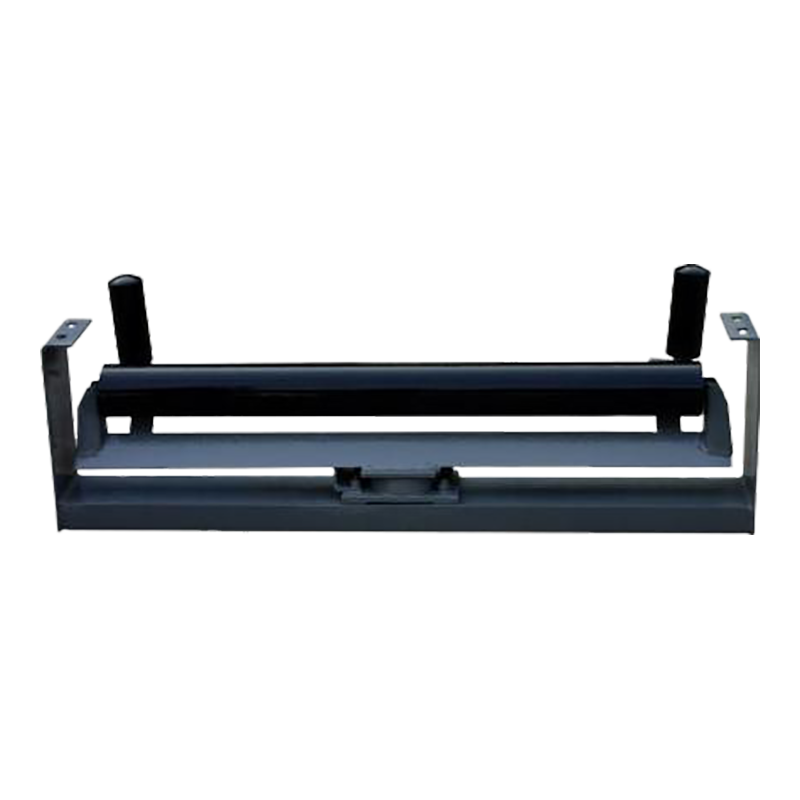
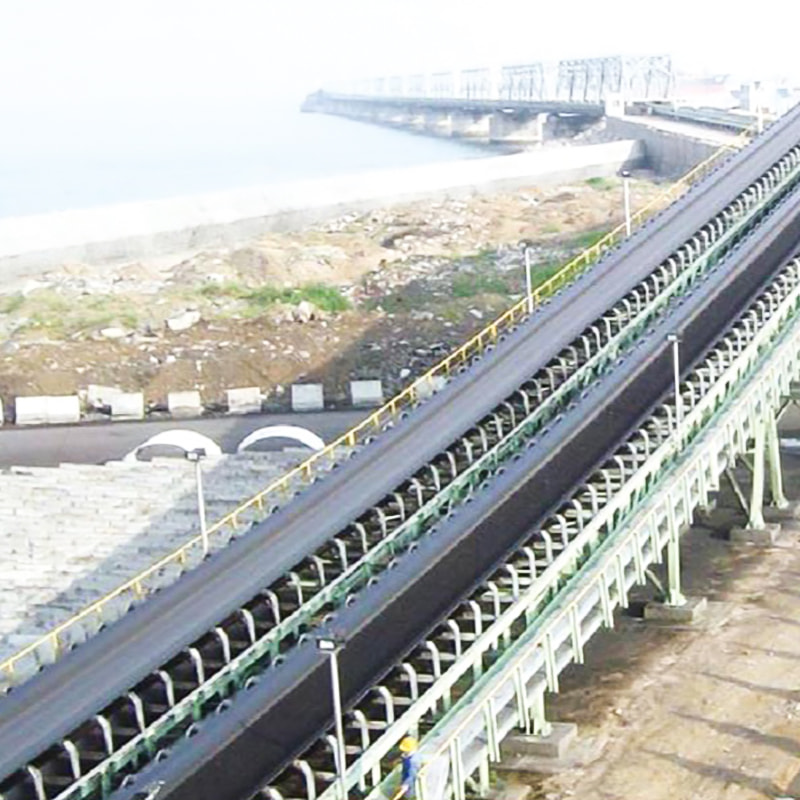
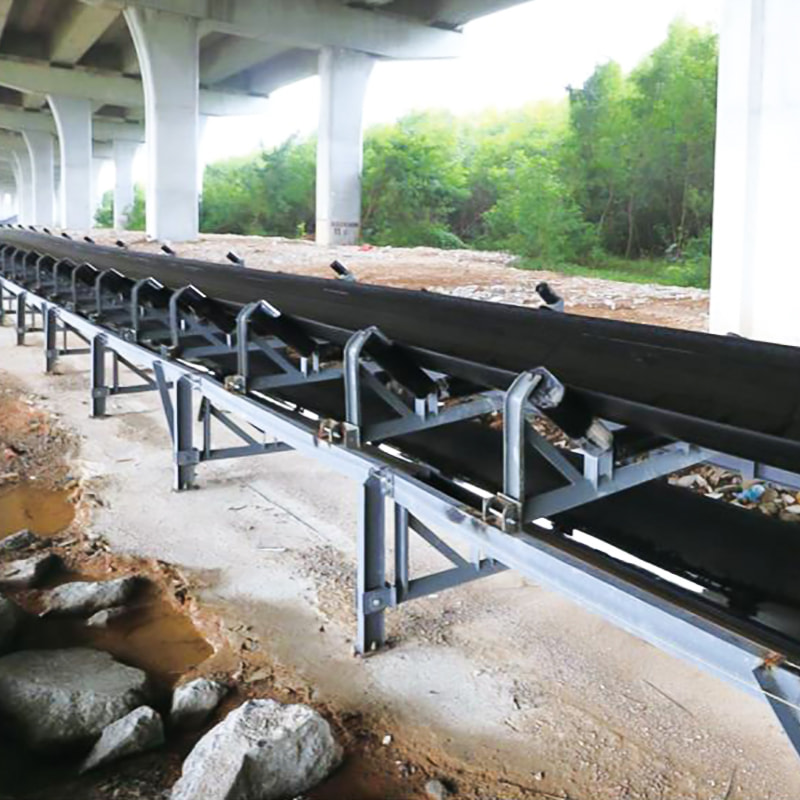
Buffer rollers are used in the receiving section of belt conveyors to reduce the impact of falling materials on the conveyor belt. Buffer rollers are installed below the receiving section of the conveyor to reduce the impact of falling materials on the conveyor belt, extend the service life of the conveyor belt, and play a role in shock absorption, buffering and support at key positions.
Content
1. Function of Belt Conveyor Buffer Rollers
(1). Buffering impact force and protecting the conveyor belt
Function: At the conveyor loading point (such as the drop port), when the material falls from a high place, a large impact force will be generated. Buffer rollers absorb the impact energy through elastic materials (such as rubber rings, springs, etc.) or special structures, reducing direct impact on the conveyor belt.
Advantage: Prevent the conveyor belt from tearing, wearing or joint damage due to long-term impact, and extend the service life.
(2). Prevent material spillage and blockage
Function: Buffer rollers are usually densely arranged or grooved to form a smooth transition at the loading point, guide the material to the center, and reduce material splashing or leakage caused by impact. Advantages: Improve conveying efficiency and reduce cleaning and maintenance costs.
(3). Reduce operating noise
Function: The elastic buffer structure can reduce the vibration and noise caused by material impact and improve the working environment.
Applicable scenarios: Areas sensitive to noise (such as indoors or near residential areas in mining areas).
(4). Support the conveyor belt and maintain stability
Function: In the impacted area (such as the loading section), the buffer roller provides additional support to prevent the conveyor belt from sagging or running off the track.
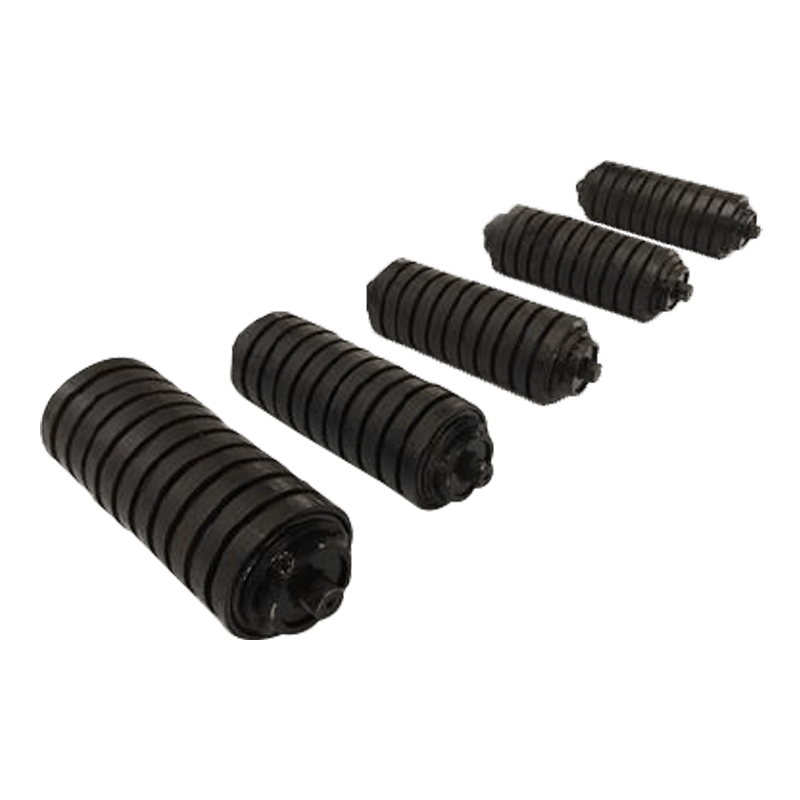
Design features: Common types include rubber ring type, spring type, polyurethane buffer roller, etc. The surface may have corrugations or grooves to enhance friction.
(5). Adapt to various material characteristics
Heavy materials (such as ore, coal): Highly elastic buffer rollers are required to resist strong impact.
Fragile materials (such as glass, food): Soft buffering is required to avoid damage.
Wet or sticky materials: Buffer rollers with anti-sticking design can be selected.
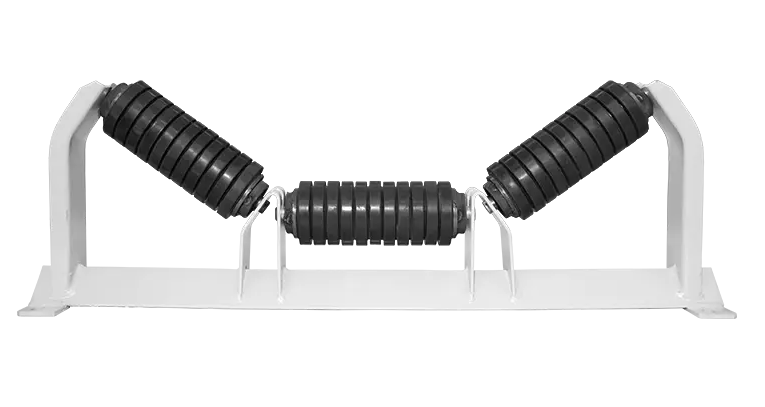
2. Differences from ordinary rollers
| Features | Impact Idler | Standard Roller |
| Material | Contains elastic elements such as rubber and springs | Metal or rigid plastic |
| Structure | With impact layer or flexible design | Rigid structure |
| Application | High-impact areas | Conventional support section |
3. Maintenance precautions for belt conveyor buffer rollers
(1). Regular Inspection
Appearance Inspection: Check whether the surface of the impact roller is cracked, deformed or severely worn (especially the rubber impact layer). Observe whether the roller rotates flexibly and whether there is any jamming or abnormal noise.
Connector Inspection: Ensure that the roller bracket, bolts and other fixings are not loose or rusted.
Frequency: It is recommended to inspect at least once a week, and the frequency should be increased under high load or harsh environment.
(2). Cleaning and Maintenance
Remove Adherent Materials: Clean dust, mud or sticky materials (such as coal, ore slag) adhered to the surface of the roller in time to prevent the roller from becoming unbalanced or wearing more seriously.
Cleaning Method: Use a high-pressure air gun or soft brush to clean, and avoid sharp tools from scratching the impact layer. For corrosive materials (such as salt, chemicals), rinse with clean water or neutral detergent and then dry.
Note: Operate when the machine is stopped to avoid safety accidents caused by cleaning during operation.
(3) Lubrication and maintenance
Bearing lubrication: For buffer rollers that need lubrication (such as models with oil filling holes), regularly add high-temperature resistant lithium-based grease to prevent dry grinding of the bearings. Remove old grease during lubrication to avoid impurities. Sealing inspection: Confirm that the bearing seals are intact to prevent moisture or dust from entering and causing bearing damage. Frequency: Lubricate once every 3 to 6 months, and shorten to 1 to 2 months in humid or dusty environments.
(4) Replacement criteria
Immediate replacement situations: The rubber buffer layer falls off or cracks severely. The roller has obvious axial movement or radial runout (>1.5mm). The rotation resistance is large (it cannot be easily rotated manually).

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español