What is a belt conveyor pulley?
 2025.08.14
2025.08.14
 Industry News
Industry News
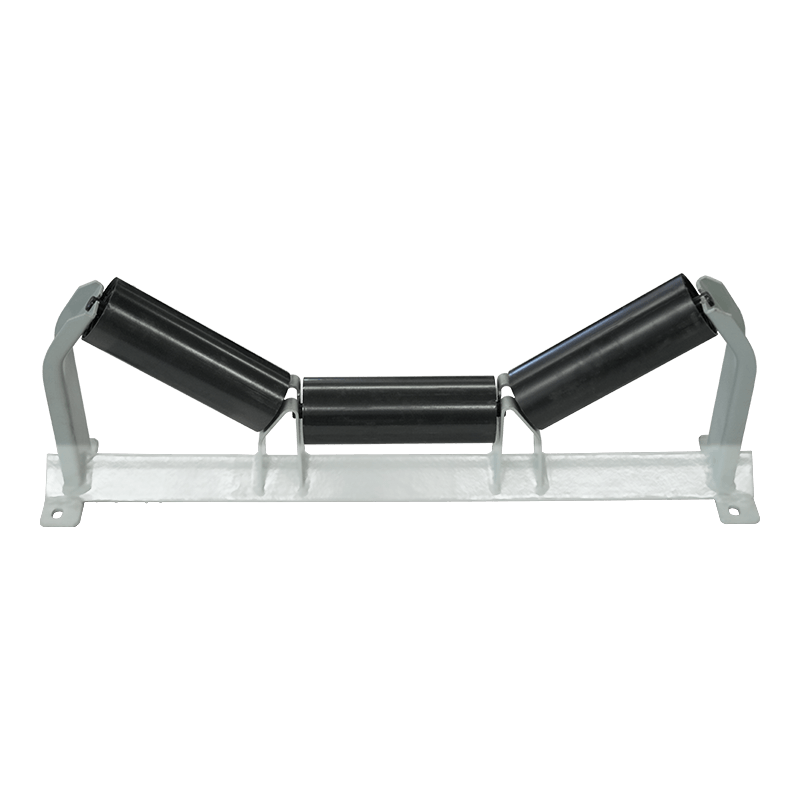
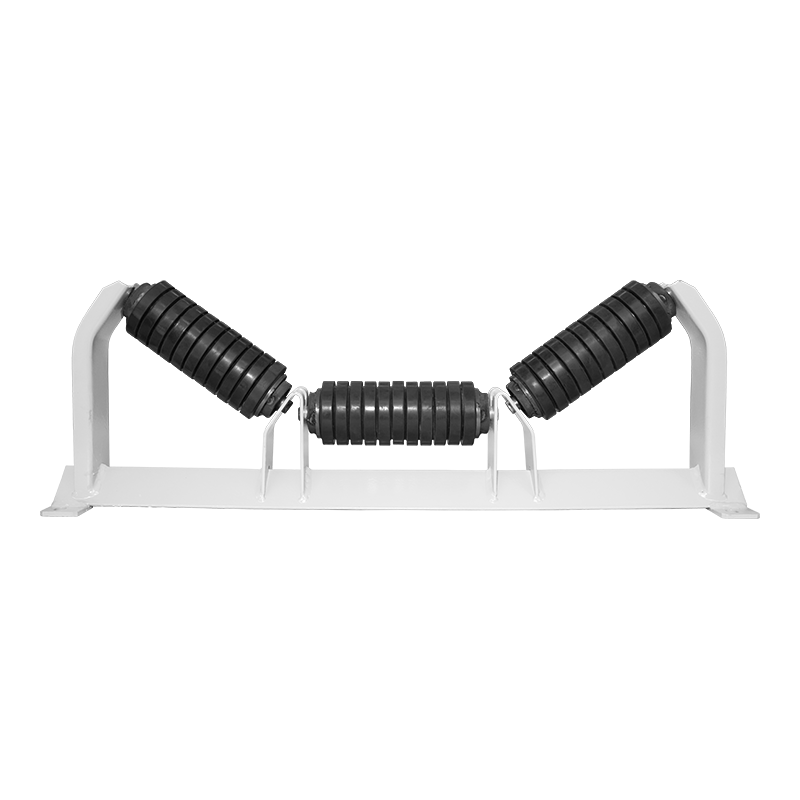
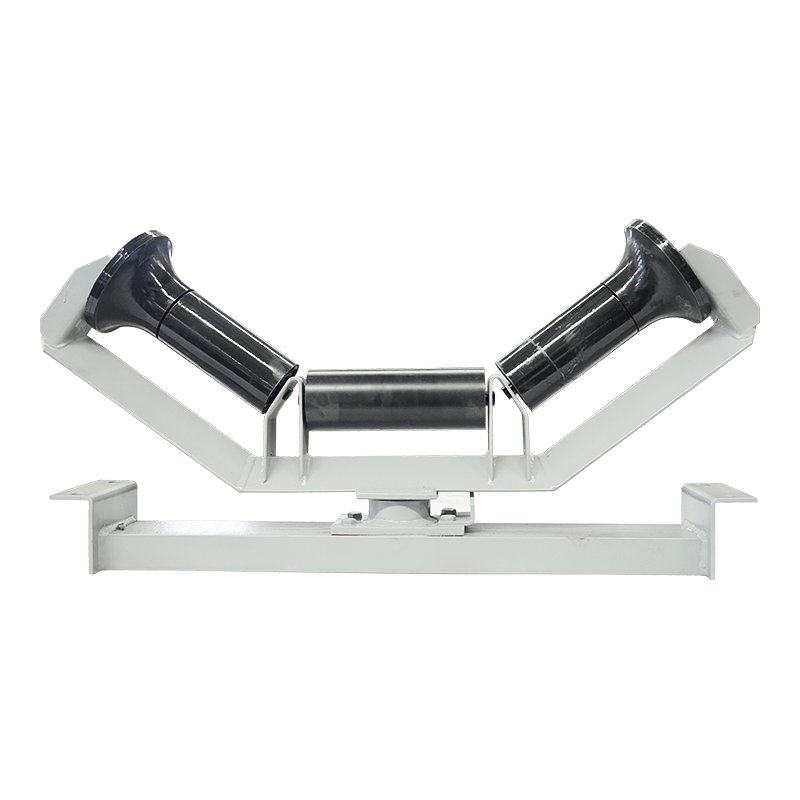
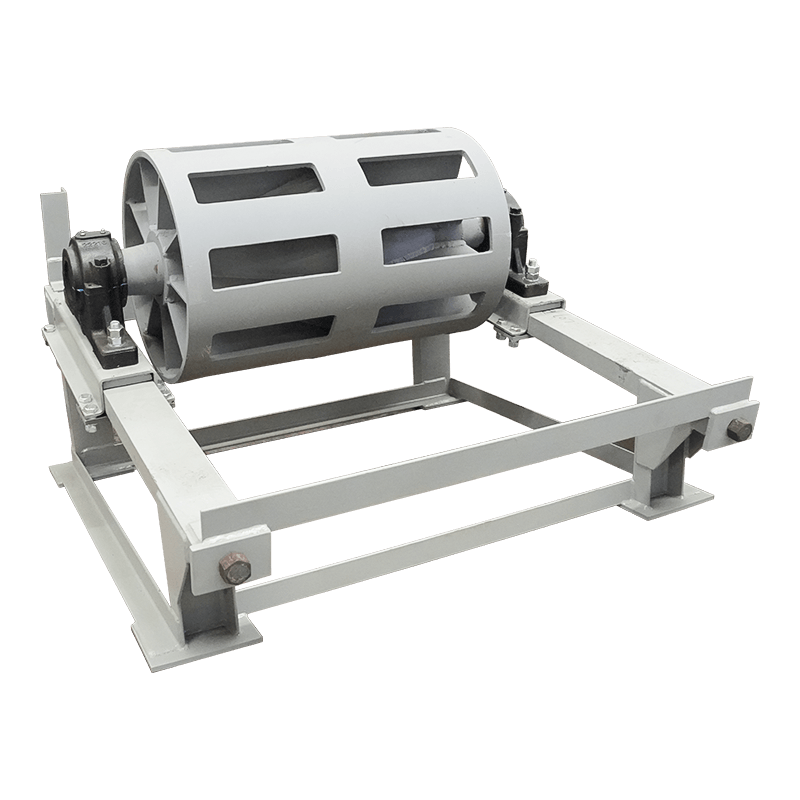
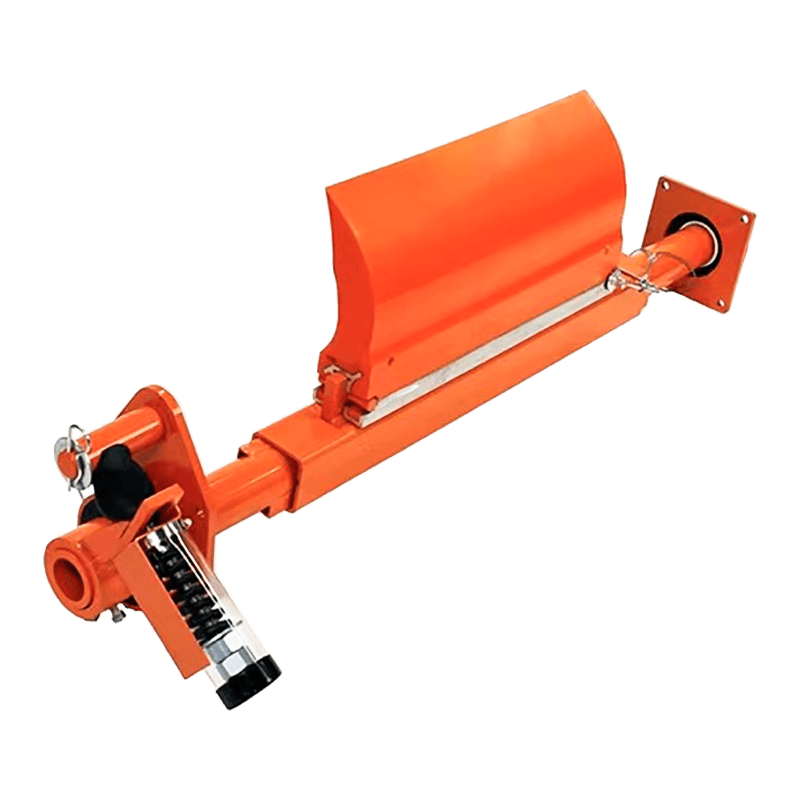
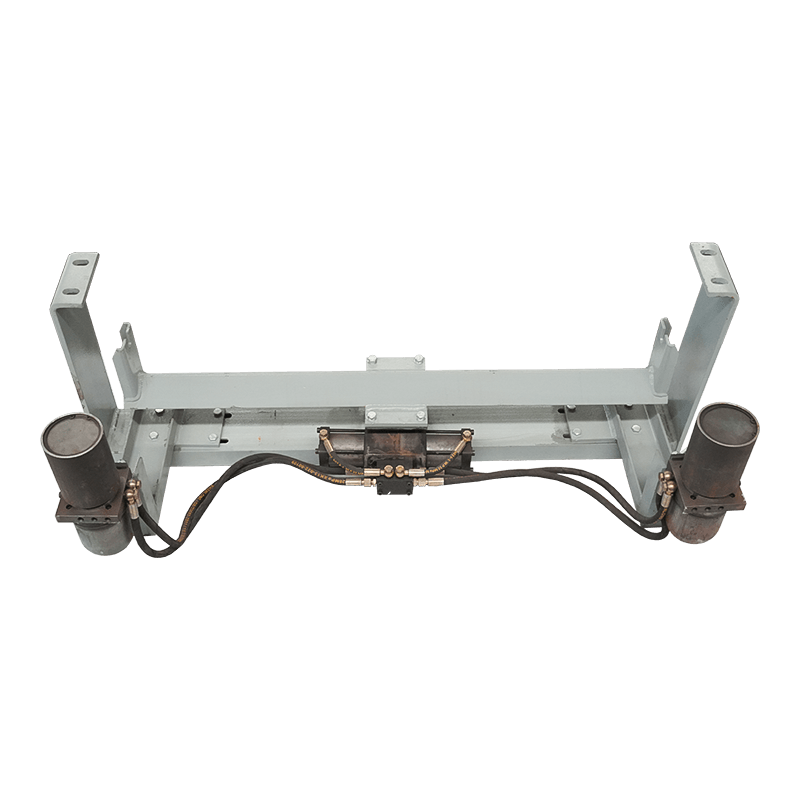
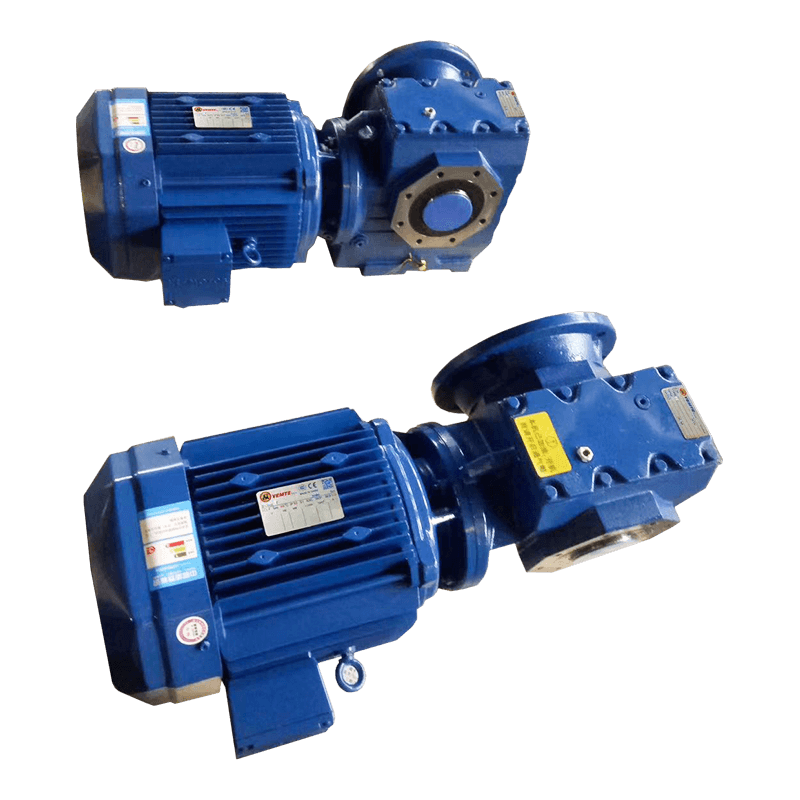
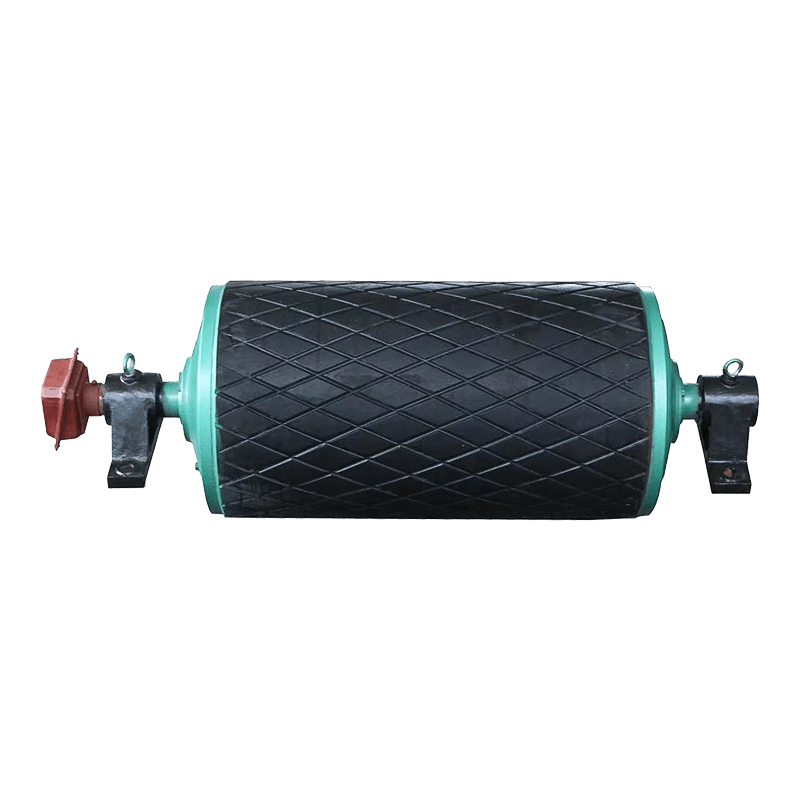
Belt conveyor pulleys are essential components of belt conveyor systems. Roller production primarily involves initial rolling of the roller body, initial static balancing, interference fit and welding of the shaft head, precision turning, and dynamic balancing. Rollers primarily support, drive, and guide the conveyor belt. They rotate to move the belt, ensuring continuous material transport. Rollers typically consist of a rigid cylinder, a center shaft, and bearings. Some are coated with materials such as rubber or ceramic to increase friction and wear resistance. Depending on their function, rollers are categorized as drive rollers, bend rollers, and tension rollers. Drive rollers connect to the power source and provide traction for the entire system; bend rollers change the direction of the conveyor belt; and tension rollers adjust the tension of the conveyor belt. The material, size, and surface treatment of these rollers are specifically designed based on the specific application (such as conveying volume, environmental conditions, and material characteristics) to ensure efficient and stable conveyor operation while minimizing belt wear and energy consumption.
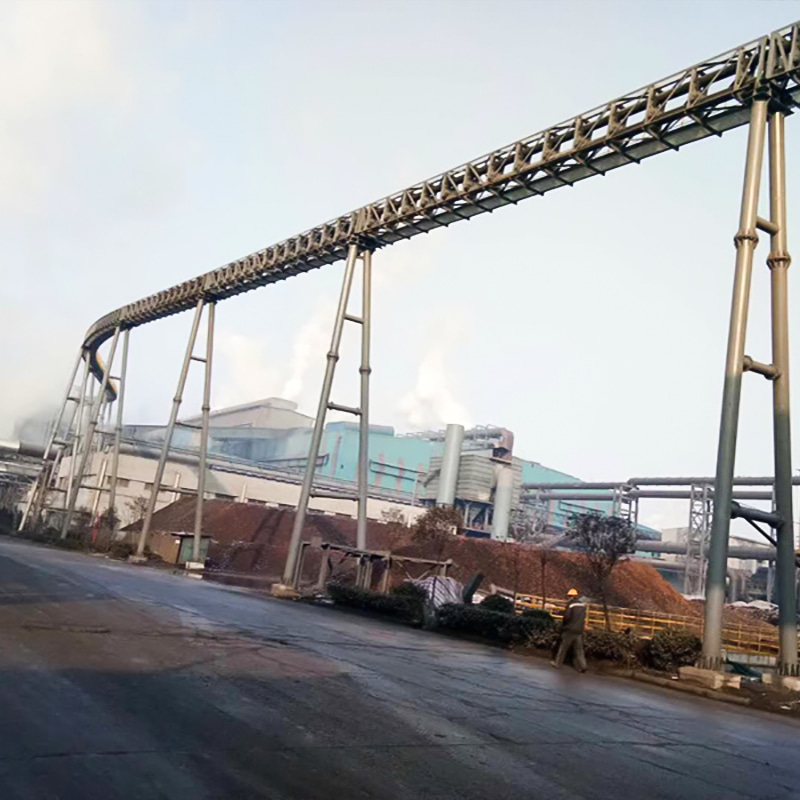
Belt conveyor pulleys are widely used in material conveying systems across various industrial sectors, encompassing diverse applications from mining and ports to food processing and chemical production. In mining, rollers support long conveyor belts transporting ore and coal. Bulk cargo handling systems at ports and terminals rely on rollers to drive massive conveyor belts for rapid cargo turnover. Cement plant raw material conveyor lines rely on high-temperature rollers for stable operation in dusty environments. In power plant coal conveyor systems, anti-static rollers ensure safe conveying. The chemical industry uses corrosion-resistant rollers to handle corrosive materials, while the food processing industry employs stainless steel or food-grade rubber-coated rollers to meet hygiene requirements. In automated sorting lines in logistics and warehousing, precision rollers enable efficient cargo diversion. Furthermore, in metallurgy, building materials, agriculture, and other fields, rollers of varying specifications adapt to diverse operating conditions, from high temperatures and humidity to extreme cold, ensuring reliable operation of conveying systems under a wide range of conditions. These rollers not only bear the enormous loads of the conveyor belt and materials, but also must cope with friction, impact, and environmental influences. Their performance directly impacts the efficiency and safety of the entire production line.

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español