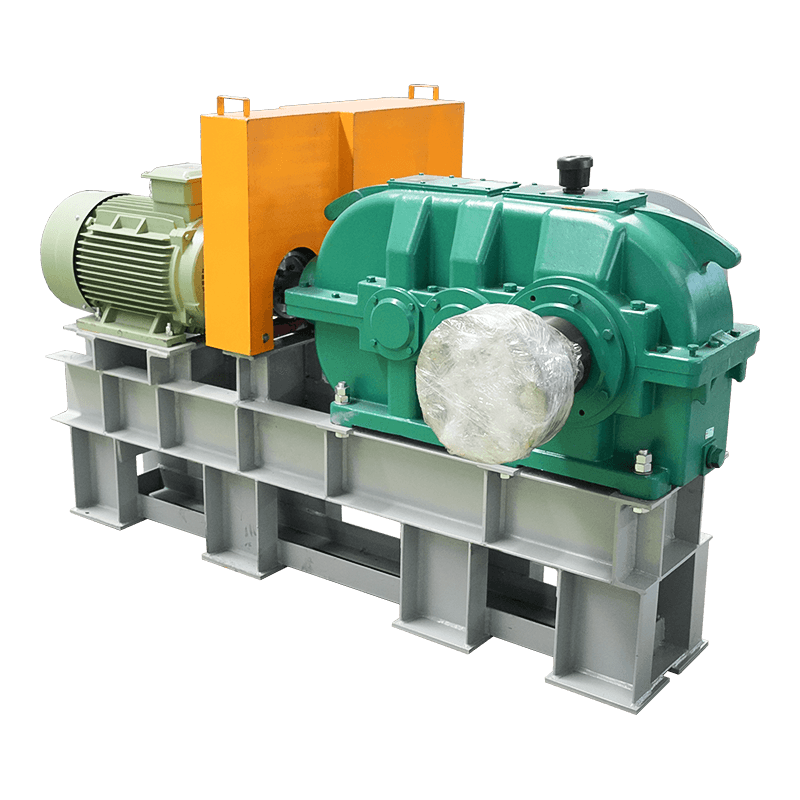
Is your spiral conveyor belt deviating or slipping? Five signs that the tensioner may be improperly adjusted
 2025.08.08
2025.08.08
 Industry News
Industry News
Content
1. Five Signs of Improper Adjustment of the Screw Conveyor Belt Tensioning Device
Signal 1: Severe wear on one side of the conveyor belt
Problem Symptoms
Asymmetrical wear on the conveyor belt edge (visible thinning or cracking on one side)
Constant belt deviation during operation
Tensioning Device Related Issues
Uneven tension on both sides: The adjustment screws of the mechanical tensioning device are not adjusted synchronously, resulting in uneven force on the conveyor belt.
Tilted guide roller installation: The guide rollers of the tensioning device are not perpendicular to the centerline of the conveyor belt, causing lateral tension.
Solution: Use a tension gauge to measure the tension on both sides of the conveyor belt and ensure the difference is ≤10%.
Recalibrate the guide rollers so that they are 90° to the direction of belt travel.
Signal 2: Intermittent belt slippage
Problem Symptoms: An abnormal "squeaking" sound is heard between the conveyor belt and the drive roller. The conveyor belt stops under a slight load, but the drive roller continues to rotate.
Tensioning Device Related Issues
Insufficient tension: The pressure of the hydraulic or spring tensioner is below the design standard (usually 50-70 N/mm²). Automatic compensation failure: The intelligent tensioning device's sensor is faulty, preventing dynamic tension adjustment.
Solution: Check the hydraulic tensioning system's pressure gauge and replenish hydraulic oil or adjust the spring preload.
Clean the tension sensor contact surface and restart the automatic compensation system.
Signal 3: Material accumulation on the conveyor belt surface
Problem manifestation: Material accumulation in a specific section of the conveyor belt (such as the head or tail).
Incomplete scraping by the cleaner, resulting in increased residual material.
Tensioning device-related issues: Locally low tension: Improper adjustment of a section of the sectional tensioning device results in localized belt slack.
Insufficient tension roller wrap angle: The tension roller is misaligned, reducing the contact area between the conveyor belt and the drive roller.
Solution: Check tension in sections, paying particular attention to the tension roller position in areas with material accumulation.
Adjust the tension roller installation angle to ensure a wrap angle of ≥180°.
Signal 4: Abnormal drive motor current fluctuations
Problem manifestations
Motor current periodically surges (exceeding the rated value by more than 15%)
Frequent inverter overload alarms
Tensioning device-related issues
Dynamic tension instability: The automatic tensioning device's response is delayed, causing the conveyor belt to momentarily slacken or overtighten.
Tensioning buffer failure: The hydraulic tensioning system's accumulator is leaking, losing its buffering function.
Solution: Test the automatic tensioning system's response time (should be ≤ 0.5 seconds) and upgrade the control program if necessary.
Check the hydraulic accumulator's air pressure and replenish nitrogen to the calibrated value.
Signal 5: Abnormal noise or vibration in the tensioning device
Problem manifestations: A clicking sound is heard from the tensioning roller bearing. The overall vibration amplitude of the tensioning frame is greater than 0.5mm.
Tensioning device-related issues
Loose mechanical structure: The locknut of the screw tensioning device is not tightened, resulting in periodic tension fluctuations.
Eccentric roller wear: The tensioning roller is subjected to uneven force over a long period of time, resulting in ovality deviation.
Solution: Tighten all mechanical connections using locknuts or threadlock.
Use a dial indicator to measure the roundness of the tension roller. If the deviation is greater than 0.1mm, the roller needs to be replaced.
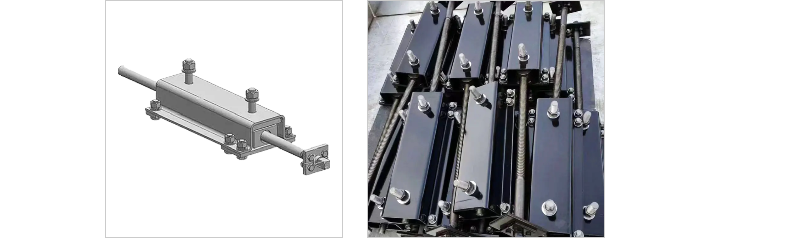
2. Screw Conveyor Belt Tensioning Device Maintenance Guide
Daily Maintenance Inspection
Visual Inspection
Inspection Frequency: Daily before startup
Inspection Details:
Is the tensioning device visible for deformation or cracks?
Is there any oil leakage in the hydraulic system?
Is there any looseness in the mechanical connectors (bolts, nuts)?
Is there any abnormal wear on the contact surface between the conveyor belt and the tensioning roller?
Operation Status Monitoring
Inspection Frequency: At least once per shift
Inspection Details:
Is there any abnormal noise during operation of the tensioning device?
Is the conveyor belt's running path centered?
Is the tensioning pressure gauge/tension indicator reading within the normal range?
Common Troubleshooting
Conveyor Belt Deviation
Possible Causes:
Uneven pressure on both sides of the tensioning device
Anomaly in the guide roller installation angle
Improper belt joint
Solution:
Re-adjust the tension on both sides
Adjust the guide roller using a laser alignment tool
Re-fabricate the conveyor belt joint
Unstable Tension
Possible Causes:
Hydraulic system internal leakage
Spring fatigue
Sensor failure
Solution:
Check the hydraulic cylinder seal
Replace the failed spring
Calibrate or replace the tension sensor
Abnormal Noise
Possible Causes:
Damaged bearing
Loose structural components
Possible Lubrication
Solution:
Replace the damaged bearing
Tighten all connecting bolts
Re-grease
3. Frequently Asked Questions about Screw Conveyor Belt Tensioning Devices
Q1: What is a screw conveyor belt tensioner?
A screw conveyor belt tensioner is a key component for maintaining proper belt tension. Through mechanical, hydraulic, or automatic adjustment, it ensures sufficient friction between the belt and the drive roller, preventing slippage and deviation.
Q2: Why is the tensioner so important to a screw conveyor system?
Preventing belt slippage ensures efficient conveying.
Reducing edge wear caused by deviation.
Extending the service life of the conveyor belt and drive components.
Maintaining system stability.
Q3: How can I determine if the tension is appropriate?
Standard method:
Using a tensiometer (recommended).
Manual inspection: Press down on the center of the conveyor belt; there should be 20-30mm of elastic deformation.
Observe the operating status: No slippage or noticeable deviation.
Q4: How can I quickly correct conveyor belt deviation?
Three-step solution:
Inspection: Confirm the deviation direction and tensioner status
Adjustment: Slightly adjust the deviation tension (≤5% each time)
Verification: Run the machine at no load for 10 minutes and observe the effect
Q5: How to address a tensioner oil leak?
Emergency Procedure:
Shut down the machine and relieve pressure
Temporarily repair with sealant
Replace the following components as soon as possible:
Hydraulic cylinder seal
Oil pipe joint gasket
Check hydraulic oil cleanliness

 English
English  русский
русский Español
Español